SLVUCZ6 November 2024 TLC69627-Q1 , TLC69628-Q1 , TLC69629-Q1 , TLC69637-Q1 , TLC69638-Q1 , TLC69639-Q1
3.5 Diagnostics
The sample code provides an API to detect which LED driver devices have faults such as Thermal Shutdown (TSD), LED open (LOD), LED short (LSD), Short-to-Ground (STG), Short-to-Power (STP), and Adjacent Pin Short (APS). For the LOD, LSD, STG, STP, and APS, the failing channel is also detected. Within the TLC6962x_3x_APIs.h file, the prototype of the API is defined.
void LED_Update_Chip_Status(void);This API updates the variable chip_status which is defined in file system_info.h.
struct busStatus {
uint16_t chip_index; // Show Chip Index
uint16_t LOD; // LED Open Detection
uint16_t LSD; // LED Short Detection
uint16_t FB_OVF; // Device FB overflow flag
uint16_t COMM_ERR; // Device communication error flag including CRC, COMM_LOSS, CMD_ERR, TOUT_ERR, MEM_ERR
uint16_t UVLO; // Device UVLO flag
uint16_t TSD; // Thermal Shutdown
uint16_t PIN_ERR; // Device PIN error flag including APS, STP, STG, ISET_O, ISET_S
uint16_t BIST; // Device BIST error flag including WDOG_BIST, TOUT_BIST, OTP_CRC
uint16_t DEV_MODE; // Device mode
uint16_t DEC; // Device FB decrease flag
uint16_t INC; // Device FB increase flag
uint16_t APS; // Device Adjacent Pin Short flag
uint16_t STG; // Device Short To Ground flag
uint16_t STP; // Device Short To Power flag
uint16_t CRC; // Device CRC flag
#if defined(_TLC696X8)
uint16_t COMM_WDOG; // Device COMM_WDOG flag
#endif
uint16_t CMD_ERR; // Device CMD_ERR flag
uint16_t TOUT_ERR; // Device time-out error fla
uint16_t ISET_O; // Device ISET open flag
uint16_t ISET_S; // Device ISET short
#if defined(_TLC696X8)
uint16_t SRAM_CRC; // Device MEM_ERR flag
uint16_t OTP_CRC; // Device OTP CRC error flag
uint16_t WDOG_BIST; // Device watchdog BIST error flag
uint16_t TOUT_BIST; // Device time-out BIST error flag
#endif
volatile OUTx LSD_channels[MAX_SCAN_LINES];
volatile OUTx LOD_channels[MAX_SCAN_LINES];
volatile OUTx APS_channels[MAX_SCAN_LINES];
volatile OUTx STG_channels[MAX_SCAN_LINES];
volatile OUTx STP_channels[MAX_SCAN_LINES];
};
struct chipStatus {
struct busStatus busStatus[MAX_CASCADED_UNITS];
};
// For diagnostics
extern struct chipStatus chip_status[BUS_NUM];The variable chip_status can be watched in the Expressions view during the debug of the code by following the steps in Watching Variables, Expressions, and Registers. An example without any error is depicted in Figure 3-3. The first index of variable chip_status is the daisy chain index. On the EVM there only 1 chain is used. For the flags of the LED drivers, the busStatus variable is used which has an index for each LED driver in the chain. On the EVM there are 2 devices cascaded and, therefore, busStatus runs from 0 to 1.
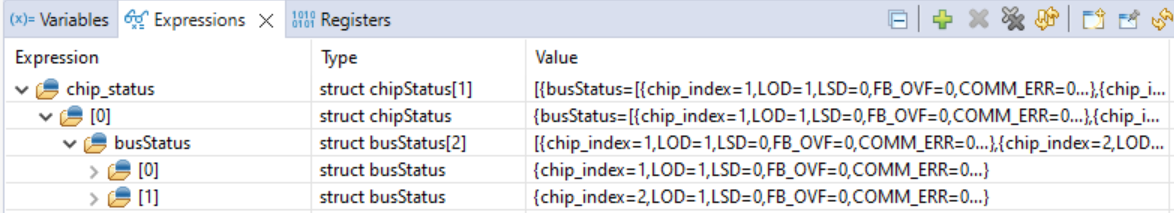 Figure 3-3 Example of Watching Expression
chip_status Without Errors
Figure 3-3 Example of Watching Expression
chip_status Without Errors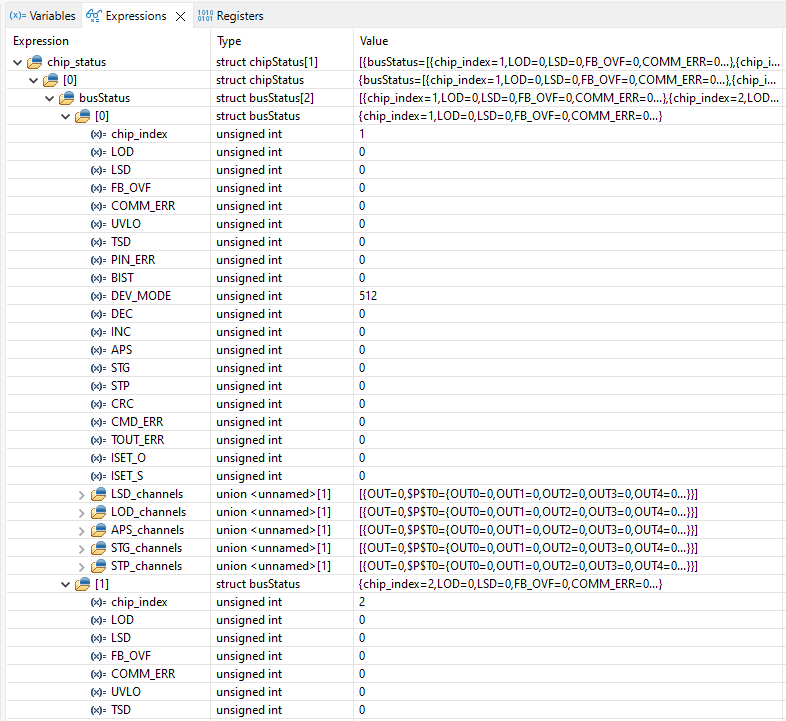 Figure 3-4 Expanded Example of Watching
Expression chip_status Without Errors
Figure 3-4 Expanded Example of Watching
Expression chip_status Without ErrorsFigure 3-4 depicts an expanded view of the chip_status variable. For each of the two LED drivers in the daisy chain, the chip index and fault status bits are shown. In addition, for the LSD, LOD, STG, STP, and APS faults the actual output channel that has the fault can be found. An example of LOD fault is depicted in Figure 3-5. In this example, chip index 1 (which is index 0 of busStatus) has an LOD fault. When array LOD_channels is expanded, it shows that the fault occurs on pin OUT15. The LOD_channels is an array with only 1 index because for the TLC6962x/TLC6963x-Q1 devices there is only 1 scan line.
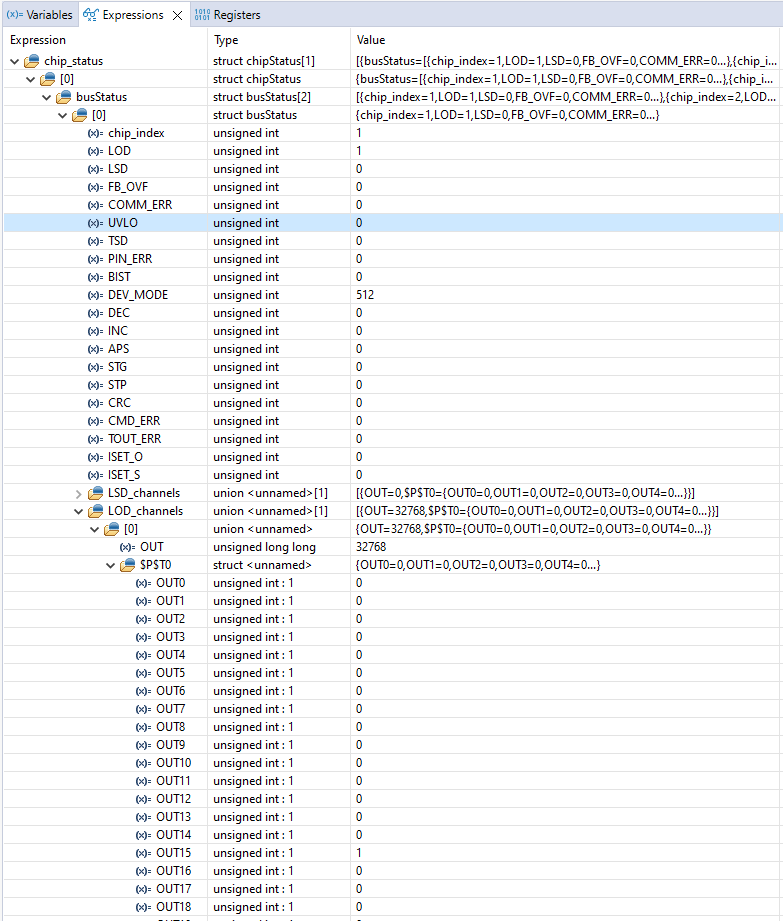 Figure 3-5 Example of chip_status With
LED Open (LOD) Fault
Figure 3-5 Example of chip_status With
LED Open (LOD) Fault